OBJECTIVES: The adenoid pad, which is located between the orifice of the Eustachian tube (ET) and posterior nasal cavity, can affect the development of otitis media with effusion (OME) because of its anatomical location. The aim of the present study was to evaluate adenoid microbial colonization through 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) pyrosequencing, an advanced molecular technique, and to document the relationship with OME.
MATERIALS and METHODS: Adenoid samples were collected using sterile cotton from 32 children during ventilation tube insertion. Sixteen children with OME who underwent tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy due to obstructive symptoms were assigned to the OME group and sixteen children without OME were assigned to the control group. We performed a 16S rRNA-based culture-independent survey of bacterial communities using the MiSeq platform.
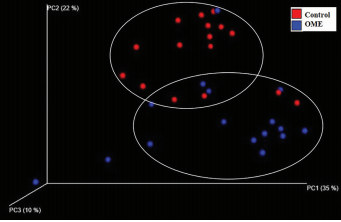
RESULTS: The diversity index, mean operational taxonomic units, and Shannon index were lower in the OME group than those in the control group. A taxonomic analysis showed differences in microbiota distribution between the OME and control groups at the phylum, genus, and species levels. The analysis, which was based on weighted UniFrac distances, revealed differences in microbial composition between the two groups.
CONCLUSION: Bacterial community analysis using 16S rRNA pyrosequencing allows us to understand the relationship between the microbial communities of adenoids and the development of OME better.
Cite this article as: Kim SK, Hong SJ, Park KH, Hong SM. Analysis of the Microbiome in the Adenoids of Korean Children with Otitis Media with Effusion. J Int Adv Otol 2019; 15(3): 379-85.


.jpg)
.png)
.png)